The respiratory epithelium is the tissue lining found in the respiratory tract. Though it is a single layer of cells along the basement membrane the alignment of the nuclei is not in the same plane and appears as multiple layers.
Be Able To Able To Label Parts Of The Respiratory System Ppt Download
Pneumonia occurs when lung defense mechanisms are diminished or overwhelmed.
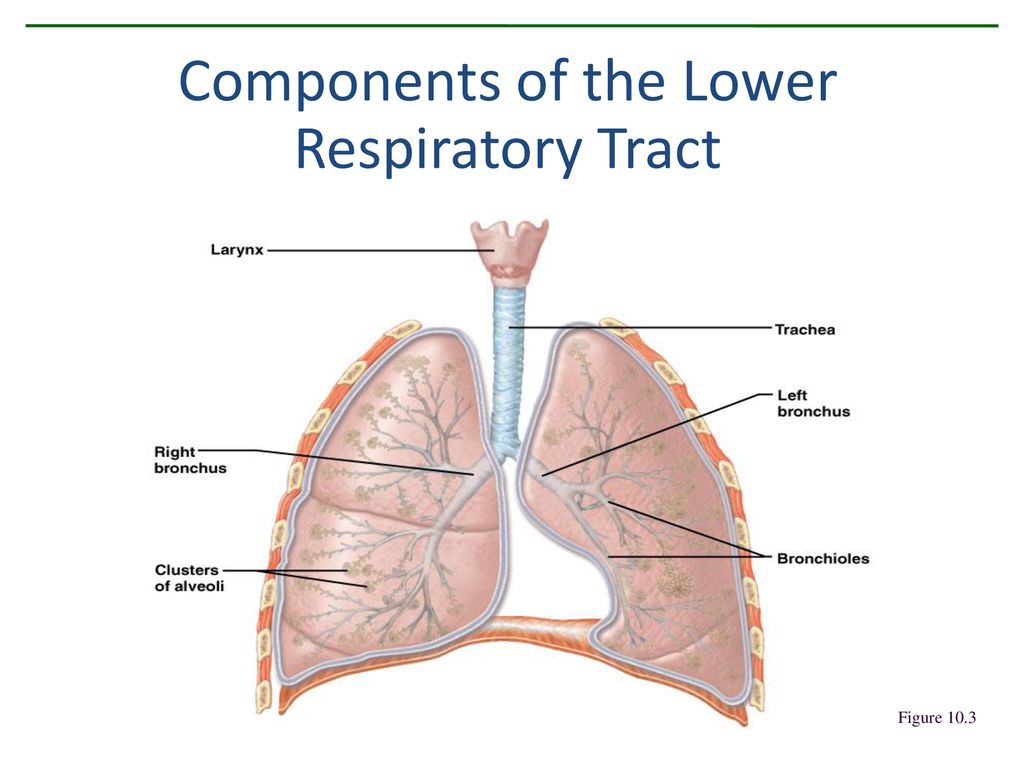
. Bronchi a pair of airways. The bronchi continue to branch into bronchial a tree. - aspirated material - excess secretions - foreign bodies.
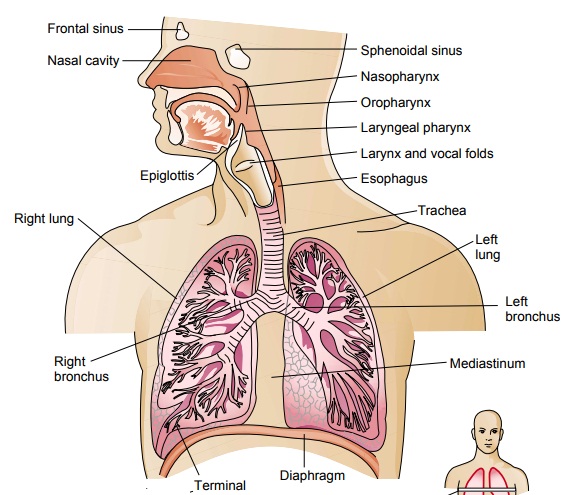
The respiratory findings observed in bronchiolitis include tachypnea wheezing crackles and rhonchi which result from inflammation of the small airways Fig. Compare and contrast the functions of upper respiratory tract with the lower respiratory tract. Describe the structures and functions of the upper and lower respiratory tracts.
Lower urinary tract symptoms LUTS is a term used to describe an array of symptoms affecting the control and quality of micturition in the lower urinary tract. Inflammatory products or foreign material from the respiratory tract distal to the larynx. LUTS can affect both men and women although they are particularly common.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Dz COPD. COPD is a term used to describe a group of pulmonary diseases of the long duration that are characterized by increased resistance to airflow which includes all of the following except. Alterations in Respiratory System Study Guide Assessment of Respiratory Function LEARNING OBJECTIVES On completion of this chapter the learner will be able to.
Term used to describe increased carbon dioxide in the blood. The upper cranial airways is lined by Psuedostratified columnar epithelium. What is the lower respiratory tract made up of.
Start studying Lower Respiratory Tract Infection. A number of terms are used to describe the function of the respiratory tract or abnormalities that arise because of a variety of diseases. Albuterol is classified as a.
Assessment of Respiratory Function Describe the structures and functions of the upper and lower respiratory Study Resources. It functions in providing moisture and protecting the airways. To accomplish this crucial function the cilia beat in coordinated metachronal waves at a beat frequency that has multiple physiological regulators.
An example of where impaired ability to cough reduces the capacity to clear tracheal respiratory secretions is. Infectious agents gain access to the lower respiratory tract by the inhalation of aerosolized material by aspiration of upper airway flora or by hematogenous seeding. It is not present in the larynx or pharynx.
The trachea bronchial tree and the lungs where gas exchange takes place. The epithelium classifies as pseudostratified. And tiny air sacs called alveoli.
Bronchitis is inflammation of the lower airways that may arise with infections eg. Alveoli alveolus the last part of the lower respiratory tract are the tiny air sacs located in clusters at the end of the bronchioles 8. BZ and S-LS are co-first author.
To catch foreign material. Bronchitis may either be acute or chronic in nature. Itis of the lungs caused by microorganism invasion of the tissue or by aspiration of foreign substances into the lower resp tract.
CI confidence interval CT computed tomography HR hazard ratio LRTI lower respiratory tract infection TFBA tracheobronchial foreign body aspiration. Smoke dust foreign material allergies diseases of the lungs etc. Acute bronchiolitis is a diagnostic term used to describe the clinical picture produced by several different viral lower respiratory tract infections in infants and very young children.
Vessels and nerves also enter the lungs. A bronchial tree or respiratory tree is the collective term used for these multiple. View Notes - Pharmacology Final - Respiratory DrugsTerm.
Bacterial viral mycoplasmal parasitic irritants eg. Respiratory epithelium is ciliated pseudostratified columnar epithelium found lining most of the respiratory tract. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools.
By TeachMeSeries Ltd 2020 Figure 1 The internal surface of the bladder highlighting the trigone. Describe ventilation diffusion perfusion and ventilationperfusion imbalances. Collectively referred to as the alveolar sacs these are surrounded by an intricate network of blood capillaries.
The main function of the cilia in the upper respiratory tract is. View Notes - Notes Exam 2- USE THESE ONESdocx from NURS 3302 at Texas State University. Describe how the respiratory system processes oxygen and CO 2.
The major symptoms or pneumonia are cough chest pain fever shortness of breath and sputum production. Or from inflammation or foreign material in the lower respiratory tract or from inhaled irritants such as tobacco smoke. Respiratory system the body system that brings oxygen from the air into the body for delivery via the blood to the Study Resources Main Menu.
It lines main nasal cavity respiratory region nasopharynx and lower part of larynx below glottis trachea and bronchi. The term acute bronchitis is used to describe an acute respiratory tract infection in which cough is the predominant feature. The lower respiratory tract consists of the lungs the organs that allow gases to move in and out of your body.
Mucociliary escalator mucous lining the upper and lower respiratory tract traps foreign particles and cilia sweep mucus and debris up and out of respiratory tract. The most common presenting sign is usually coughing. Cilia are specialized organelles that provide the force necessary to transport foreign materials in the respiratory tract toward the mouth where they can be swallowed or expectorated.

Anatomy And Normal Microbiota Of The Respiratory Tract Microbiology
0 Comments